If you were surprised by the outcome of the recent US Presidential
elections, you can imagine the surprise of the “expert” pollsters whose alleged
expertise it is, to predict these events. These predictions were based on an
understanding of the population (the data), which in this case meant predicting
how 120 million people would vote based on a sample of 25,000 or maybe 100,000 people
who are assumed to be a representative sample. They were
all wrong because the sample was simply not representative of the actual voting
population. So it goes. It is very easy to go wrong with big data even when you have deep expertise.
This is not so different from Google claiming “human quality MT” based on a sample of 500 sentences. Unfortunately for them, it is just not true once you step away from these 500 sentences. The real world is much more unpredictable.
This is a guest post by Juan Rowda about Corpus Analysis which is a technical way of saying it is about understanding your data in a serious MT use case scenario. Juan has special expertise with corpus analysis as he is involved in a translation project that is attempting to translate billions of words where this type of analysis is critical. And, unlike the boys at Google, who shout hooray with 500 sentences that look good, the linguists at eBay judge themselves on how well they are doing with 60 million product listings across 12,000 categories and so are less likely to be shouting hooray until many millions of sentences are looking good.They also have millions of people looking at the translations so I am sure get regular feedback when the MT is not good. This post is more demanding at a technical level than many of the posts on eMpTy Pages, but I hope that you will find it useful.
This is not so different from Google claiming “human quality MT” based on a sample of 500 sentences. Unfortunately for them, it is just not true once you step away from these 500 sentences. The real world is much more unpredictable.
This is a guest post by Juan Rowda about Corpus Analysis which is a technical way of saying it is about understanding your data in a serious MT use case scenario. Juan has special expertise with corpus analysis as he is involved in a translation project that is attempting to translate billions of words where this type of analysis is critical. And, unlike the boys at Google, who shout hooray with 500 sentences that look good, the linguists at eBay judge themselves on how well they are doing with 60 million product listings across 12,000 categories and so are less likely to be shouting hooray until many millions of sentences are looking good.They also have millions of people looking at the translations so I am sure get regular feedback when the MT is not good. This post is more demanding at a technical level than many of the posts on eMpTy Pages, but I hope that you will find it useful.
-----------------
Statistical
Machine Translation (SMT) needs considerably big amounts of text data to
produce good translations. We are talking about millions of words. But it’s not
simply any text data – it’s good data that will produce good translations. Does
“garbage in, garbage out” ring a bell?
In this scenario, and speaking mainly from a linguist’s perspective, the challenge is how to make sense of all of these millions of words? What to do to find out whether the quality of a corpus is good enough to be used in your MT system? How do you know what to improve if you realize a corpus is not good? How to know what your corpus is about?
In this article, I will cover some analysis techniques and tips that I believe are useful and effective to understand your corpus better. Please note that, to keep things simple, I will call corpus to any text sample, either used to produce translations or being the result of a translation-related process.
AntConc and Python can be used in Windows, Mac and Linux.
AntConc
As defined by its website, AntConc is a freeware corpus analysis toolkit for concordancing and text analysis. It’s really simple to use, it contains 7 main tools for analysis and has several interesting features. We will take a closer look at the details and how the tool can be used with the following examples.
Getting a Word List
A great way to know more about your corpus is getting a list of all the words that appear in it. AntConc can easily create a list with all the words that appear in your corpus, and show important additional information about them, like how many tokens are there and the frequency of each. Knowing which words appear in your corpus can help you identify what it is about; the frequency can help you determine which are the most important words.
You can also see how many tokens (individual words) and word types (unique words) are there in a corpus. This is important to determine how varied (how many different words) your text is.
To create a Word List, after loading your corpus file(s), click the Word List tab and click Start. You’ll see a list of words sorted by frequency by default. You can change the sorting order in the Sort by drop down. Besides frequency, you can sort alphabetically and by word ending.
Frequency is often a good indicator of important words - it makes sense to
assume that tokens that appear many times have a more relevant role in the text.
But what about prepositions or determiners and other words that don’t really add any meaning to the analysis? You can define a word list range, i.e., you can add stopwords (words you want to exclude from your analysis) individually or entire lists.
Word lists are also a very good resource to create glossaries. You can either use the frequency to identify key words or just go through the list to identify words that may be difficult to translate.
Keyword Lists
This feature allows you to compare a reference corpus and a target corpus, and calculate words that are unusually frequent or infrequent. What’s the use for this? Well, this can help you get a better insight on post-editing changes, for example, and try to identify words and phrases that were consistently changed by post-editors. It’s safe to assume that the MT system is not producing a correct translation for such words and phrases. You can add these to any blacklists, QA checks, or automated post-editing rules you may be using.
A typical scenario would be this: you use your MT output as target corpus, and post-edited/ human translation (for the same source text, of course) as source corpus; the comparison will tell you which words are frequent in the MT output that are not so frequent in the PE/HT content.
Vintage here is at the top of the list. In my file with MT output segments, it occurs 705 times. If I do the same with the post-edited content, there are 0 occurrences. This means post-editors have consistently changed “vintage” to something else. It’s safe to add this word to my blacklist then, as I’m sure I don’t want to see it in my translated content. If I know how it should be translated, it could be part of an automated post-processing rule. Of course, if you are training your engine with the post-edited content, “vintage” should become less common in the output.
To add a reference corpus, in the Tool Preferences menu, select Add Directory or Add Files to choose your corpus file(s). Click the Load button after adding your files.
Collocates
Collocates are simply words that occur together. This feature allows you to search for a word in a corpus and get a list of results that show other words that appear next to the search term. You can see how frequent a collocate is and also choose if results should include collocates appearing to the right of the term, to the left, or both. What’s really interesting about this is that it can help you find occurrences of words that occur near your search term, and not necessarily next to it. For example, in eBay’s listing titles, the word clutch can be sometimes mistranslated. It’s a polysemous word and it can be either a small purse or an auto part. I can do some analysis on the collocate results for clutch (auto parts) and see if terms like bag, leather, purse, etc., occur near it.
You can also select how frequent a collocate needs to be in order to be included in the results.
This is very useful to spot unusual combinations of words, as well. It obviously depends on the language, but a clear example could be a preposition followed by another preposition.
To use this feature, load your corpus files, and click the Collocates tab. Select the From and To ranges - values here contain a number and a letter: L(eft)/R(ight). The number indicates how many words away from the search terms should be included in the results, and L/R indicates the direction in which collocates must appear. You can also select a frequency value. Enter a search term and click start.
All the results obtained with any of the tools AntConc provides can be exported into several formats. This allows you to take your data and process it in any other tool.
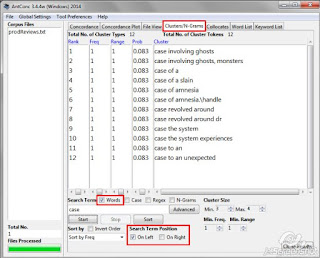
Clusters/N-Grams
This is perhaps one of the most useful features in AntConc. Why? Because it allows you to find patterns. Remember that, when working with MT output, most of the times it’s not realistic to try to find and/or fix every single issue. There may be tons of errors with varying levels of severity in the MT output (especially considering the volumes of content processed by MT), so it does make sense to focus first on those that occur more frequently or that have a higher severity.
Here's a simple example: let’s assume that by looking at your MT output you realize that your MT system is translating the word “inches” into “centimeters”, without making any changes to the numbers that usually precede that word, i.e., 10 inches is being consistently translated as 10 centimeters. You could try to find and fix 1 centimeter, 2 centimeters, 3 centimeters, etc. Rather, a much better choice would be to identify a pattern: “any number” followed by the word “centimeter” should be instead “any number” “inches”. This is an oversimplification, but the point is that identifying an error pattern is a much better approach than fixing individual errors.
Once you have identified a pattern, the next step is to figure out how you can create some sort of rule to find/fix such pattern. Simple patterns made of word or phrases are pretty straightforward - find all instances of “red dress” and replace with “blue dress”, for example. Now, you can take this to the next level by using regular expressions. Going back to the inches example you could easily find all instances of “any number” followed by centimeters with a simple regex like \d+ centimeters, where \d stands for any number and the + signs stands for 1 or more (numbers).
Clusters
Using the Clusters/N-Grams tool helps you find strings of text based on their length (number of tokens or words), frequency, and even the occurrence of any specific word. Once you open your corpus, AntConc can find a word or a pattern in it and cluster the results in a list. If you search for a word in your corpus, you can opt to see words that precede or follow the word you searched for.
Results can be sorted:
We can also use regular expressions here for cases in which we need more powerful searches. Remember the example about numbers and inches above? Well, numbers, words, spaces, letters, punctuation - all these can be covered with regular expressions.
Let’s take a look at a few examples:
Here, I want to see all 2-word clusters that start with the word “original”, so I’m going to use a boundary (\b) before “original”. I don’t know the second word, it’s actually what I want to find out, so I’m going to use \w, which stands for “any word”. All my results will then have the following form: original+word.
The n-gram search is definitely an advantage when you don’t know your corpus very well and you still don’t know what kind of issues to expect. It’s usually a good choice if it’s the first time you are analyzing a corpus - it finds patterns for you: common expressions, repeated phrases, etc.
When working with n-grams, it’s really important to consider frequency. You want to focus your analysis on n-grams that occur frequently first, so you can cover a higher number of issues.
What can you do with your findings, besides the obvious fact of knowing your corpus better? You can find recurring issues and create automated post-editing rules. Automated post-editing is a technique that consists in applying search and replace operations on the MT output. For instance, going back to our initial inches vs. centimeters example, you could create a rule that replaces all instances of number+centimeters with number+inches. Using regular expressions, you can create very powerful, flexible rules. Even though this technique was particularly effective when working with RBMT, it’s still pretty useful for SMT between training cycles (the process in which you feed new data to your system so it learns to produce better translations).
You can also create blacklists with issues found in your MT output. A blacklist is simply a list of terms that you don’t want to see in your target so, for example, if your system is consistently mistranslating the word “case” as a legal case instead of a protective case, you can add the incorrect terms to the blacklists and easily detect when they occur in your output. In the same way, you can create QA checks to run in tools like Checkmate or Xbench.
Python
For those of you not familiar with it, Python is a programming language that has been gaining more and more popularity for several reasons: it's easy to learn and easy to read, it can be run in different environments and operating systems, and there is a significant number of modules that can be imported and used.
Modules are files that contain classes, functions, and other data. Without getting too technical, a module is code already written that you can reuse, without having to write it yourself from scratch. Quick example: if you want to write a program that will use regular expressions, you can simply import the re module and Python will learn how to deal with them thanks to the data in the module.
I'm not a Python expert myself, and I apologize if the terminology I use here is not what experts use.
Enter Natural Language Processing Toolkit
Modules are the perfect segue to introduce the Natural Language Processing Toolkit (nltk). Let me just steal the definition from their site, www.nltk.org: NLTK is a leading platform for building Python programs to work with human language data. It provides easy-to-use interfaces to over 50 corpora and lexical resources such as WordNet, along with a suite of text processing libraries for classification, tokenization, stemming, tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning, wrappers for industrial-strength NLP libraries[...].
Using Python and NLTK, there's quite a few interesting things you can do to learn more about your corpora. I have to assume you are somewhat familiar with Python (not an expert!), as a full tutorial would simply exceed the purpose of this post. If you want to learn more about it, there are really good courses on Coursera, Udemy, Youtube, etc. I personally like Codeacademy's hands-on approach.
You have two options here: you can choose to use corpora provided by NLTK (ideal if you just want to try these examples, see how Python works, etc.) or you can use your own files. Let me walk you through both cases.
If you want to use corpora from NLTK, open your Python's IDLE, import the nltk module (you'll do this every time you want to use nltk) and then download the corpora:
A new window will open, and you'll be able to download one or more corpora, as well as other packages. You can find the entire list here.
When working in Python, you can import (a) all available corpora at the same time or (b) a single corpus. Notice that (a) will import books (like Moby Dick, The Book of Genesis, etc...)
If you want to use your own files, you'll have to tell Python where they are, so it can read them. Follow these steps if you want to work with one file (remember to import nltk!):
Basically, I'm telling Python to open my file called reviews.txt saved in C: (the "r" in front of the path is required for Python to read it correctly). I'm also telling Python I want to read, not write on, this file.
Then, I'm asking Python to read the contents of my file and store them in a variable called "raw"; to tokenize the content ("identify" the words in it) and to store those tokens in a variable text. Don't get scared by the technical lingo at this point: a variable is just a name that we assign to a bucket where we store information, so we can later make reference to it.
What if you have more than one file? You can use the Plain Text Corpus Reader to deal with several plaintext documents. Note that, if you follow the example below, you'll need to replace the red sections with the relevant information, like your path, your file extension, etc...
Here, I'm asking Python to import PlaintextCorpusReader, that my files have the TXT extension, where the files are stored, and to store the data from my files into a variable called corpus.
You can test if your data was correctly read just by typing the name of the variable containing it:
corpus and text are the variables I used to store data in the examples above.
Analyzing (finally!)
Now that we are all set up, and have our corpora imported, let's see some of the things we can do to analyze it:
We can get a wordcount using the "len" function. It is important to know the size of our corpus, basically to understand what we are dealing with. What we'll obtain is a count of all words and symbols, repeated words included.
If we wanted to count unique tokens, excluding repeated elements:
With the "set" function, we can get a list of all the words used in our corpus, i.e., a vocabulary:
A list of words is definitely useful, but it's usually better to have them alphabetically sorted. We can also do that easily:
Note that Python will put capitalized words at the beginning of your list.
We can check how many times a word is used on average, what we call lexical richness. From a corpus analysis perspective, it's good that a corpus is lexically rich as, theoretically, the MT system will "learn" how to deal with a broader range of words. This indicator can be obtained by dividing the total number of words by the number of unique words:
If you need to find out how many times a word occurs in your corpus, you can try the following (notice this is case-sensitive):
One key piece of information you probably want to get is the number of occurrences of each token or vocabulary item. As we mentioned previously, frequent words say a lot about your corpus, they can be used to create glossaries, etc. One way to do this is using frequency distributions. You can also use this method to find how many times a certain word occurs.
A similar way to do this is using the vocab function:
Conversely, if you wanted to see the words that only appear one time:
If you only want to see, for example, the 10 most common tokens from your corpus, there's a function for that:
We can have the frequency distributions results presented in many ways:
Here, I'm using a for loop. Loops are typically used when you want to repeat or iterate and action. In this case, I'm asking Python, for each token or sample in my corpus, to print said sample. The loop will perform the same action for all the tokens, one at the time, and stop when it has covered every single one of them.
Let’s say now that you want to obtain ngrams. There are many methods, but here is a very simple one:
In this example, I’m using a sentence (mytext) for clarity purposes, but you can use a longer text or a file. What I’m doing is splitting the text based on the value of the n variable, in this case, 3. This way, I can print all the trigrams in my text.
If I wanted to get bigrams instead, I can simply change the value of n:
To close this post, let’s take a look at how you can filter out stopwords. These are very common, high-frequency words in any language, like prepositions or possessive pronouns. For example, if you want to see a list of the most “important” words in your corpus, or if you are trying to create a glossary, words like “the” or “my” barely have any lexical value. You don't need them.
NLTK includes a corpus with more than 2,400 stopwords for 11 languages. You can import this corpus and see its content:
Let’s try this on our own corpus. Again, I’m going to use a sentence, but you can try this on files too:
One of the benefits of filtering out stopwords is that you will reduce the size of your corpus, making it easier to work with. In the example above, we reduced our sentence from 51 to 35 tokens.
In this scenario, and speaking mainly from a linguist’s perspective, the challenge is how to make sense of all of these millions of words? What to do to find out whether the quality of a corpus is good enough to be used in your MT system? How do you know what to improve if you realize a corpus is not good? How to know what your corpus is about?
It’s simply unrealistic to try to understand your corpus by reading every single line or word in it.
Corpus analysis can help you find answers to these questions. It can also help you understand how your MT system is performing and why. It can even help you understand how your post-editors are performing.
In this article, I will cover some analysis techniques and tips that I believe are useful and effective to understand your corpus better. Please note that, to keep things simple, I will call corpus to any text sample, either used to produce translations or being the result of a translation-related process.
The Tools
I’m going to cover two tools: AntConc and Python. The first one is a corpus analysis tool exclusively. The latter is a programming language (linguists, please, don't panic!), but I’m going to show you how you can use a natural language processing module (NLTK) to dig into your corpora, and provide snippets of code for you to try.AntConc and Python can be used in Windows, Mac and Linux.
AntConc
As defined by its website, AntConc is a freeware corpus analysis toolkit for concordancing and text analysis. It’s really simple to use, it contains 7 main tools for analysis and has several interesting features. We will take a closer look at the details and how the tool can be used with the following examples.
Getting a Word List
A great way to know more about your corpus is getting a list of all the words that appear in it. AntConc can easily create a list with all the words that appear in your corpus, and show important additional information about them, like how many tokens are there and the frequency of each. Knowing which words appear in your corpus can help you identify what it is about; the frequency can help you determine which are the most important words.
You can also see how many tokens (individual words) and word types (unique words) are there in a corpus. This is important to determine how varied (how many different words) your text is.
To create a Word List, after loading your corpus file(s), click the Word List tab and click Start. You’ll see a list of words sorted by frequency by default. You can change the sorting order in the Sort by drop down. Besides frequency, you can sort alphabetically and by word ending.
But what about prepositions or determiners and other words that don’t really add any meaning to the analysis? You can define a word list range, i.e., you can add stopwords (words you want to exclude from your analysis) individually or entire lists.
Word lists are also a very good resource to create glossaries. You can either use the frequency to identify key words or just go through the list to identify words that may be difficult to translate.
Keyword Lists
This feature allows you to compare a reference corpus and a target corpus, and calculate words that are unusually frequent or infrequent. What’s the use for this? Well, this can help you get a better insight on post-editing changes, for example, and try to identify words and phrases that were consistently changed by post-editors. It’s safe to assume that the MT system is not producing a correct translation for such words and phrases. You can add these to any blacklists, QA checks, or automated post-editing rules you may be using.
A typical scenario would be this: you use your MT output as target corpus, and post-edited/ human translation (for the same source text, of course) as source corpus; the comparison will tell you which words are frequent in the MT output that are not so frequent in the PE/HT content.
Vintage here is at the top of the list. In my file with MT output segments, it occurs 705 times. If I do the same with the post-edited content, there are 0 occurrences. This means post-editors have consistently changed “vintage” to something else. It’s safe to add this word to my blacklist then, as I’m sure I don’t want to see it in my translated content. If I know how it should be translated, it could be part of an automated post-processing rule. Of course, if you are training your engine with the post-edited content, “vintage” should become less common in the output.
To add a reference corpus, in the Tool Preferences menu, select Add Directory or Add Files to choose your corpus file(s). Click the Load button after adding your files.
Collocates
Collocates are simply words that occur together. This feature allows you to search for a word in a corpus and get a list of results that show other words that appear next to the search term. You can see how frequent a collocate is and also choose if results should include collocates appearing to the right of the term, to the left, or both. What’s really interesting about this is that it can help you find occurrences of words that occur near your search term, and not necessarily next to it. For example, in eBay’s listing titles, the word clutch can be sometimes mistranslated. It’s a polysemous word and it can be either a small purse or an auto part. I can do some analysis on the collocate results for clutch (auto parts) and see if terms like bag, leather, purse, etc., occur near it.
You can also select how frequent a collocate needs to be in order to be included in the results.
This is very useful to spot unusual combinations of words, as well. It obviously depends on the language, but a clear example could be a preposition followed by another preposition.
To use this feature, load your corpus files, and click the Collocates tab. Select the From and To ranges - values here contain a number and a letter: L(eft)/R(ight). The number indicates how many words away from the search terms should be included in the results, and L/R indicates the direction in which collocates must appear. You can also select a frequency value. Enter a search term and click start.
All the results obtained with any of the tools AntConc provides can be exported into several formats. This allows you to take your data and process it in any other tool.
Clusters/N-Grams
This is perhaps one of the most useful features in AntConc. Why? Because it allows you to find patterns. Remember that, when working with MT output, most of the times it’s not realistic to try to find and/or fix every single issue. There may be tons of errors with varying levels of severity in the MT output (especially considering the volumes of content processed by MT), so it does make sense to focus first on those that occur more frequently or that have a higher severity.
Here's a simple example: let’s assume that by looking at your MT output you realize that your MT system is translating the word “inches” into “centimeters”, without making any changes to the numbers that usually precede that word, i.e., 10 inches is being consistently translated as 10 centimeters. You could try to find and fix 1 centimeter, 2 centimeters, 3 centimeters, etc. Rather, a much better choice would be to identify a pattern: “any number” followed by the word “centimeter” should be instead “any number” “inches”. This is an oversimplification, but the point is that identifying an error pattern is a much better approach than fixing individual errors.
Once you have identified a pattern, the next step is to figure out how you can create some sort of rule to find/fix such pattern. Simple patterns made of word or phrases are pretty straightforward - find all instances of “red dress” and replace with “blue dress”, for example. Now, you can take this to the next level by using regular expressions. Going back to the inches example you could easily find all instances of “any number” followed by centimeters with a simple regex like \d+ centimeters, where \d stands for any number and the + signs stands for 1 or more (numbers).
Clusters
Using the Clusters/N-Grams tool helps you find strings of text based on their length (number of tokens or words), frequency, and even the occurrence of any specific word. Once you open your corpus, AntConc can find a word or a pattern in it and cluster the results in a list. If you search for a word in your corpus, you can opt to see words that precede or follow the word you searched for.
Results can be sorted:
- by frequency (ideal to find recurring patterns - the more frequent a pattern is, the more relevant it might be),
- by word (ideal to see how your MT system is dealing with the translation of a particular term),
- by word end (sorted alphabetically based off the last word in the string),
- by range (if your corpus is composed of more than one file, in how many of those files the search term appears), and
- by transitional probability (how likely it is that word2 will occur after word1; e.g., the probability of “Am” occurring after “I” is much higher than “dishwasher” occurring after “I”.).
On Left
On Right
We can also use regular expressions here for cases in which we need more powerful searches. Remember the example about numbers and inches above? Well, numbers, words, spaces, letters, punctuation - all these can be covered with regular expressions.
Let’s take a look at a few examples:
Here, I want to see all 2-word clusters that start with the word “original”, so I’m going to use a boundary (\b) before “original”. I don’t know the second word, it’s actually what I want to find out, so I’m going to use \w, which stands for “any word”. All my results will then have the following form: original+word.
Now, I want to see all clusters, regardless of their frequency, that contain
the words “price” OR “quality”. So, in addition to adding the boundaries, I’m
going to separate these words with | that simply stands for “or”.
This is really useful when you want to check how the system is dealing with certain words - there’s no need to run separate searches since you can combine any number of words with | between them. Check the Global Settings menu for reference.
For seasoned regex users, note that regex capabilities in AntConc are pretty modest and that some operators are not standard.
N-grams
If you are not familiar with this term, in a nutshell, an n-gram is any word or sequence of words of any size; a 1-gram is composed of one element, a 2-gram is composed of 2 elements, etc. It’s a term that defines the length of a string rather than its content.
What’s great about this feature is that you can find recurring phrases
without specifying any search terms. That is, you can easily obtain a list of,
for example, all the 6-grams to 3-grams that occur more than 10 times in your
corpus. Remember that clusters work in the opposite way - you find words that
surround a specific search term.This is really useful when you want to check how the system is dealing with certain words - there’s no need to run separate searches since you can combine any number of words with | between them. Check the Global Settings menu for reference.
For seasoned regex users, note that regex capabilities in AntConc are pretty modest and that some operators are not standard.
N-grams
If you are not familiar with this term, in a nutshell, an n-gram is any word or sequence of words of any size; a 1-gram is composed of one element, a 2-gram is composed of 2 elements, etc. It’s a term that defines the length of a string rather than its content.
The n-gram search is definitely an advantage when you don’t know your corpus very well and you still don’t know what kind of issues to expect. It’s usually a good choice if it’s the first time you are analyzing a corpus - it finds patterns for you: common expressions, repeated phrases, etc.
When working with n-grams, it’s really important to consider frequency. You want to focus your analysis on n-grams that occur frequently first, so you can cover a higher number of issues.
What can you do with your findings, besides the obvious fact of knowing your corpus better? You can find recurring issues and create automated post-editing rules. Automated post-editing is a technique that consists in applying search and replace operations on the MT output. For instance, going back to our initial inches vs. centimeters example, you could create a rule that replaces all instances of number+centimeters with number+inches. Using regular expressions, you can create very powerful, flexible rules. Even though this technique was particularly effective when working with RBMT, it’s still pretty useful for SMT between training cycles (the process in which you feed new data to your system so it learns to produce better translations).
You can also create blacklists with issues found in your MT output. A blacklist is simply a list of terms that you don’t want to see in your target so, for example, if your system is consistently mistranslating the word “case” as a legal case instead of a protective case, you can add the incorrect terms to the blacklists and easily detect when they occur in your output. In the same way, you can create QA checks to run in tools like Checkmate or Xbench.
Python
For those of you not familiar with it, Python is a programming language that has been gaining more and more popularity for several reasons: it's easy to learn and easy to read, it can be run in different environments and operating systems, and there is a significant number of modules that can be imported and used.
Modules are files that contain classes, functions, and other data. Without getting too technical, a module is code already written that you can reuse, without having to write it yourself from scratch. Quick example: if you want to write a program that will use regular expressions, you can simply import the re module and Python will learn how to deal with them thanks to the data in the module.
I'm not a Python expert myself, and I apologize if the terminology I use here is not what experts use.
Enter Natural Language Processing Toolkit
Modules are the perfect segue to introduce the Natural Language Processing Toolkit (nltk). Let me just steal the definition from their site, www.nltk.org: NLTK is a leading platform for building Python programs to work with human language data. It provides easy-to-use interfaces to over 50 corpora and lexical resources such as WordNet, along with a suite of text processing libraries for classification, tokenization, stemming, tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning, wrappers for industrial-strength NLP libraries[...].
Using Python and NLTK, there's quite a few interesting things you can do to learn more about your corpora. I have to assume you are somewhat familiar with Python (not an expert!), as a full tutorial would simply exceed the purpose of this post. If you want to learn more about it, there are really good courses on Coursera, Udemy, Youtube, etc. I personally like Codeacademy's hands-on approach.
The Mise en Place
= To follow these examples, you'll need the following installed:- Python 3.5 (version 2.7 works too, but some of these examples may need tweaking)
- NLTK
- Numpy (optional)
You have two options here: you can choose to use corpora provided by NLTK (ideal if you just want to try these examples, see how Python works, etc.) or you can use your own files. Let me walk you through both cases.
If you want to use corpora from NLTK, open your Python's IDLE, import the nltk module (you'll do this every time you want to use nltk) and then download the corpora:
>>> import nltk
>>> nltk.download()
A new window will open, and you'll be able to download one or more corpora, as well as other packages. You can find the entire list here.
When working in Python, you can import (a) all available corpora at the same time or (b) a single corpus. Notice that (a) will import books (like Moby Dick, The Book of Genesis, etc...)
a >>> from nltk.book import *
b >>> from nltk.corpus import brown
If you want to use your own files, you'll have to tell Python where they are, so it can read them. Follow these steps if you want to work with one file (remember to import nltk!):
>>> f = open(r'c:\reviews.txt','rU')
>>> raw = f.read()
>>> tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(raw)
>>> text = nltk.Text(tokens)
Basically, I'm telling Python to open my file called reviews.txt saved in C: (the "r" in front of the path is required for Python to read it correctly). I'm also telling Python I want to read, not write on, this file.
Then, I'm asking Python to read the contents of my file and store them in a variable called "raw"; to tokenize the content ("identify" the words in it) and to store those tokens in a variable text. Don't get scared by the technical lingo at this point: a variable is just a name that we assign to a bucket where we store information, so we can later make reference to it.
What if you have more than one file? You can use the Plain Text Corpus Reader to deal with several plaintext documents. Note that, if you follow the example below, you'll need to replace the red sections with the relevant information, like your path, your file extension, etc...
>>> from nltk.corpus import PlaintextCorpusReader
>>> files = ".*\.txt"
>>> corpus0 = PlaintextCorpusReader(r"C:/corpus", files)
>>> corpus = nltk.Text(corpus0.words())
Here, I'm asking Python to import PlaintextCorpusReader, that my files have the TXT extension, where the files are stored, and to store the data from my files into a variable called corpus.
You can test if your data was correctly read just by typing the name of the variable containing it:
>>> corpus
<Text: This black and silver Toshiba Excite is a...>
>>> text
<Text:`` It 's a Motorola StarTac , there...>
corpus and text are the variables I used to store data in the examples above.
Analyzing (finally!)
Now that we are all set up, and have our corpora imported, let's see some of the things we can do to analyze it:
We can get a wordcount using the "len" function. It is important to know the size of our corpus, basically to understand what we are dealing with. What we'll obtain is a count of all words and symbols, repeated words included.
>>> len(text)
43237
>>> len(corpus)
610
If we wanted to count unique tokens, excluding repeated elements:
>>> len(set(corpus))
370
With the "set" function, we can get a list of all the words used in our corpus, i.e., a vocabulary:
>>> set(corpus)
{'knowledge', 'Lord', 'stolen', 'one', ':', 'threat', 'PEN', 'gunslingers', 'missions', 'extracting', 'ensuring',
'Players', 'player', 'must', 'constantly', 'except', 'Domino', 'odds', 'Core', 'SuperSponge', etc..
A list of words is definitely useful, but it's usually better to have them alphabetically sorted. We can also do that easily:
>>> sorted(set(corpus))
["'", '(', ').', ',', '-', '--', '.', '3', '98', ':', 'Ancaria', 'Apocalypse', 'Ashen',
'Barnacle', 'Bikini', 'Black', 'Bond', 'Bottom', 'Boy', 'Core', 'Croft', 'Croy', 'D',
'Dalmatian', 'Domino', 'Egyptian', etc...
Note that Python will put capitalized words at the beginning of your list.
We can check how many times a word is used on average, what we call lexical richness. From a corpus analysis perspective, it's good that a corpus is lexically rich as, theoretically, the MT system will "learn" how to deal with a broader range of words. This indicator can be obtained by dividing the total number of words by the number of unique words:
>>> len(text)/len(set(text))
6.1459843638948115
>>> len(corpus)/len(set(corpus))
1.6486486486486487
If you need to find out how many times a word occurs in your corpus, you can try the following (notice this is case-sensitive):
>>> text.count("leave")
50
>>> text.count("Leave")
10
One key piece of information you probably want to get is the number of occurrences of each token or vocabulary item. As we mentioned previously, frequent words say a lot about your corpus, they can be used to create glossaries, etc. One way to do this is using frequency distributions. You can also use this method to find how many times a certain word occurs.
>>> fdistcorpus = FreqDist(corpus)
>>> fdistcorpus
FreqDist({',': 33, 'the': 27, 'and': 24, '.': 20, 'a': 20, 'of': 17, 'to': 16, '-': 12,
'in': 8, 'is': 8, ...})
>>> fdistcorpus['a']
20
A similar way to do this is using the vocab function:
>>> text.vocab()
FreqDist({',': 2094, '.': 1919, 'the': 1735, 'a': 1009, 'of': 978, 'and': 912, 'to': 896, 'is': 597,
'in': 543, 'that': 518, ...})
Conversely, if you wanted to see the words that only appear one time:
>>> fdistcorpus.hapaxes()
['knowledge', 'opening', 'mystical', 'return', 'bound']
If you only want to see, for example, the 10 most common tokens from your corpus, there's a function for that:
>>> fdistcorpus.most_common(10)
[(',', 33), ('the', 27), ('and', 24), ('.', 20), ('a', 20), ('of', 17), ('to', 16), ('-', 12), ('in', 8),
('is', 8)]
We can have the frequency distributions results presented in many ways:
- one column:
>>> for sample in fdistcorpus:
print(sample)
knowledge
opening
mystical
return
bound
moving
Bottom
slam
Lord
Ms
Here, I'm using a for loop. Loops are typically used when you want to repeat or iterate and action. In this case, I'm asking Python, for each token or sample in my corpus, to print said sample. The loop will perform the same action for all the tokens, one at the time, and stop when it has covered every single one of them.
- tab-separated:
>>> fdistcorpus.tabulate()
, the and .
a of to
- chart
Let’s say now that you want to obtain ngrams. There are many methods, but here is a very simple one:
>>> from nltk import ngrams
>>> mytext = "I’m
selling these fine leather jackets"
>>> n = 3
>>> trigrams = ngrams(mytext.split(),n)
>>> for grams in trigrams:
print(grams)
('I’m', 'selling', 'these')
('selling', 'these', 'fine')
('these', 'fine', 'leather')
('fine', 'leather', 'jackets')In this example, I’m using a sentence (mytext) for clarity purposes, but you can use a longer text or a file. What I’m doing is splitting the text based on the value of the n variable, in this case, 3. This way, I can print all the trigrams in my text.
If I wanted to get bigrams instead, I can simply change the value of n:
>>>
n = 2
>>>
bigrams = ngrams(mytext.split(),n)
>>>
for
grams in bigrams:
print(grams)
('I’m', 'selling')
('selling', 'these')
('these', 'fine')
('fine', 'leather')
('leather', 'jackets')
TIP: use this formula to easily calculate the number of ngrams in a sentence:
number of words – ngram + 1
Example: I’m selling these fine leather jackets
6 (words) – 3 (trigrams) + 1 = 4 trigrams
1
- ('I’m',
'selling',
'these')
2
-('selling',
'these',
'fine')
3
- ('these',
'fine',
'leather')
4
-('fine',
'leather',
'jackets')To close this post, let’s take a look at how you can filter out stopwords. These are very common, high-frequency words in any language, like prepositions or possessive pronouns. For example, if you want to see a list of the most “important” words in your corpus, or if you are trying to create a glossary, words like “the” or “my” barely have any lexical value. You don't need them.
NLTK includes a corpus with more than 2,400 stopwords for 11 languages. You can import this corpus and see its content:
>>> from nltk.corpus import stopwords
>>> stopwords.words('spanish')
['de', 'la', 'que', 'el', 'en', 'y', 'a', 'los', 'del', 'se', 'las', 'por', 'un', 'para', 'con', 'no',
>>>
stopwords.words('italian')
['ad', 'al', 'allo', 'ai', 'agli', 'all', 'agl', 'alla', 'alle', 'con', 'col', 'coi'...Let’s try this on our own corpus. Again, I’m going to use a sentence, but you can try this on files too:
>>>
from
nltk.corpus import stopwords
>>>
from
nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
>>>
mytext="Shepard was born
on April 11, 2154,[1] is a graduate of the Systems
Alliance N7 special forces program (service no. 5923-AC-2826), a veteran of the
Skyllian Blitz, and is initially assigned to the SSV Normandy in 2183 as
Executive Officer."
>>>
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
>>>
word_tokens = word_tokenize(mytext)
>>>
filtered_sentence = [w for w in word_tokens
if
not
w in
stop_words]
>>>
for
w in
word_tokens:
if w not in stop_words:
filtered_sentence.append(w)
>>> print(filtered_sentence)
['Shepard', 'born', 'April', '11', ',', '2154', ',', '[', '1', ']', 'graduate', 'Systems', 'Alliance', 'N7', 'special', 'forces', 'program', '(', 'service', '.', '5923-AC-2826', ')', ',', 'veteran', 'Skyllian', 'Blitz', ',', 'initially', 'assigned', 'SSV', 'Normandy', '2183', 'Executive', 'Officer', '.']
>>>
print(word_tokens)
['Shepard', 'was', 'born', 'on', 'April', '11', ',', '2154', ',', '[', '1', ']', 'is', 'a', 'graduate', 'of', 'the', 'Systems', 'Alliance', 'N7', 'special', 'forces', 'program', '(', 'service', 'no', '.', '5923-AC-2826', ')', ',', 'a', 'veteran', 'of', 'the', 'Skyllian', 'Blitz', ',', 'and', 'is', 'initially', 'assigned', 'to', 'the', 'SSV', 'Normandy', 'in', '2183', 'as', 'Executive', 'Officer', '.']One of the benefits of filtering out stopwords is that you will reduce the size of your corpus, making it easier to work with. In the example above, we reduced our sentence from 51 to 35 tokens.
>>> len(filtered_sentence)
35
>>> len(word_tokens)
51
There is so much you can do with Python and NLTK that it would be impossible
to cover everything in this post. If you are interested in learning more, I
encourage you to check out the book “Natural Language Processing with Python:
Analyzing Text with the Natural Language Toolkit”.
-------
Juan Rowda
Staff MT Language Specialist, eBay
https://www.linkedin.com/in/juan-martín-fernández-rowda-b238915
Juan is a certified localization professional working in the localization industry since 2003. He joined eBay in 2014. Before that, he worked as translator/editor for several years, managed and trained a team of +10 translators specialized in IT, and also worked as a localization engineer for some time. He first started working with MT in 2006. Juan helped to localize quite a few major video games, as well.
He was also a professional CAT tool trainer and taught courses on localization.
Juan holds a BA in technical, scientific, legal, and literary translation.
-------
Juan Rowda
Staff MT Language Specialist, eBay
https://www.linkedin.com/in/juan-martín-fernández-rowda-b238915
Juan is a certified localization professional working in the localization industry since 2003. He joined eBay in 2014. Before that, he worked as translator/editor for several years, managed and trained a team of +10 translators specialized in IT, and also worked as a localization engineer for some time. He first started working with MT in 2006. Juan helped to localize quite a few major video games, as well.
He was also a professional CAT tool trainer and taught courses on localization.
Juan holds a BA in technical, scientific, legal, and literary translation.











No comments:
Post a Comment